AI in Cybersecurity: Improving Both Defenses and Risk
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the cybersecurity landscape.
On one hand, AI is bolstering cyber defenses, giving security professionals powerful tools to detect, prevent, and respond to threats more effectively.
On the other, AI is also creating new and sophisticated risks at an alarming scale, with 96% of business executives believing AI will play a role in enabling a security breach in their organisation within the next three years.
In this feature of the VENZA Echo, we review the dual impact of AI on cybersecurity, exploring both the increasing threats and the enhanced defenses it brings.
Bolstering Defenses
The use of AI in cybersecurity is booming, with projections estimating that the market will reach a staggering $133.8 billion by 2030. It’s not just spending that is increasing—adoption is as well. More than 70% of enterprises are already testing these novel solutions in their organisations.
It’s not hard to see why. Traditional security measures often rely on predefined rules and manual monitoring, requiring a huge allocation of time and resources from understaffed teams. AI automates these processes, offering real-time threat detection and response capabilities that are far more efficient and accurate.
AI-powered tools now focus on four key areas:
Threat Detection and Response
By analyzing vast amounts of data in real time, AI solutions can identify suspicious activities and potential breaches. Advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms can recognize patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyberattack, allowing immediate response and mitigation efforts.
Predictive Analytics
New AI solutions use predictive analytics to foresee potential threats before they occur. With its capability to process and analyze vast amounts of data, AI tools review historical data from previous attacks to prevent new ones.
Advanced systems are even moving towards behavioral analysis of hackers, examining data to detect attack patterns. This involves measuring everything from the timing and methods of attacks to the movements hackers make once inside systems, enabling a more proactive and comprehensive approach to cybersecurity.
Risk & Vulnerability Monitoring
AI-powered tools are highly effective at conducting comprehensive risk and vulnerability assessments. These systems continuously scan networks, systems, and applications to detect weaknesses and potential points of exploitation.
By leveraging ML algorithms and vast datasets, AI tools can identify vulnerabilities that traditional methods might miss, prioritizing them based on their severity and potential impact.
Security Automation
By automating routine tasks, AI solutions significantly increase the efficiency of already strained IT security teams. With automatic threat detection and incident response, the scale of repetitive tasks can be minimized, freeing teams to focus on more complex and strategic aspects of security.
Rising Threats
As security teams worldwide harness the power of AI to fortify their defenses, cybercriminals are exploiting the same technology for nefarious gain.
AI’s widespread availability has allowed hackers to ramp up the volume and sophistication of their attacks to unprecedented levels. For example, free AI-powered tools like WormGPT and FraudGPT are emerging on the dark web, making it easier than ever for cybercriminals to launch sophisticated, large-scale attacks.
This has raised concern in many expert circles, including the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) which warned businesses to remain vigilant. Further, 75% of cybersecurity professionals have seen an increase in attacks in the past year, with 85% attributing this rise to generative AI.
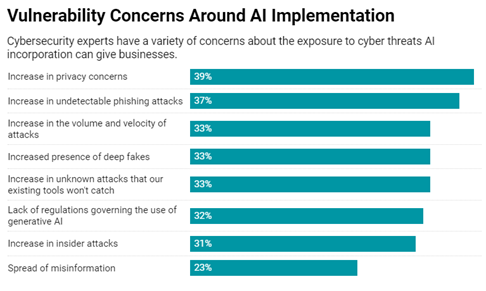
Source: Sapio Research & Deep Instinct
With this in mind, some key emerging threats include:
Enhanced Social Engineering Attacks
AI-generated content and tactics represent a new frontier in social engineering. Advanced tools, like ChatGPT, are being exploited on the dark web, enabling hackers to create highly personalized and convincing phishing and smishing attempts with ease. These sophisticated attacks are designed to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
Generative AI is rapidly changing the face of phishing emails. Although phishing attempts comprise 3 billion or 1.2% of all daily emails, improved spam filters and widespread training and awareness campaigns have kept victim counts relatively low. However, hallmarks of phishing, like grammatical mistakes and spelling errors, may be wiped clean by AI language models.
Gone are the days of the obvious scams like Nigerian Prince emails, replaced with convincingly polished emails that can even bypass sophisticated spam filters. Moreover, it’s not just email security that will need updating to counter this threat; training on how to identify these insidious emails will also need to be revisited entirely.
Even more concerning is the rise of AI impersonation, where threat actors use AI technologies to mimic the voices of loved ones or trusted individuals over the phone. As the AI voice cloning tools are readily available and incredibly convincing, these scams are already sweeping the globe. A recent McAfee study found that 1 in 10 individuals had already been targeted by this threat, with 77% of victims losing money as a direct result. Typically, these scams involve spear-phishing attempts, where attackers pose as a victim’s loved one over the phone to urgently request money. However, a recent robocall in New Hampshire took a different approach by impersonating President Joe Biden, urging voters not to participate in the presidential primary.
AI-Powered Malware
A significant and unprecedented threat is the development of AI-enabled malware. This type of malicious software, commonly found in suspicious hyperlinks, can adapt to security measures in real time, changing its behavior to avoid detection. As it learns from its environment, it becomes more effective at infiltrating systems, stealing data, and causing damage.
So far, this threat has mostly remained theoretical with few real-world examples of AI malware in use. However, using AI large language models (LLM)s, researchers have successfully developed polymorphic malware. This malicious software mutates and modifies its code each time it infects a new system, making it near-impossible to detect by security professionals and antivirus alike.
Researchers warn that feeding LLMs malware source code could generate numerous polymorphic variants, each equally dangerous, potentially overwhelming security professionals. Given that malware overtook ransomware as the preferred method for network attacks in 2023, this is a threat that should not be overlooked.
Intrusion Attacks
While malware represents one type of intrusion attack, it certainly isn’t the only one that is becoming increasingly sophisticated with the help of AI. Intrusion attacks include a wide range of methods, including worms, trojans ransomware, and simple Denial of Service (DoS).
Cybercriminals have been able to automate and enhance traditional intrusion methods, making them harder to detect and prevent. AI can analyze network traffic patterns, identify vulnerabilities, and execute attacks with precision, often outpacing traditional security measures and easily compromising an organisation’s systems or network.
Researchers have already created a potentially devastating AI worm that steals data and deploys malware simultaneously, with UK security experts warning of AI-powered ransomware threats on the horizon.
Volume
AI’s capacity to automate and scale operations means that the volume of cyberattacks is increasing. Cybercriminals can launch numerous attacks simultaneously, targeting multiple organisations or individuals. In a recent assessment, the National Cyber Security Centre in the UK estimates that AI-fueled cyber-attacks will “almost certainly” increase and deliver higher impact over the next two years.
This increased volume puts additional strain on IT security teams, who must manage and respond to a higher number of incidents. The sheer scale of attacks can overwhelm traditional security measures, necessitating the adoption of AI-driven defense mechanisms to keep pace.
AI Platforms Vulnerabilities
One of the most prevalent threats to businesses is the use of AI technologies themselves. As we discussed in last week’s feature, many businesses have already employed third-party AI platforms to enhance customer relations and operational efficiency. These solutions require large amounts of personal data to learn and function effectively, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
This issue is already widespread, with a study from HiddenLayer revealing that 77% of companies reported a breach of their AI systems in the past year. OpenAI has even acted, terminating the accounts of five state-affiliated threat actors who were using their services for malicious cybersecurity deeds.
The vulnerabilities extend beyond third-party vendors to the inherent nature of machine learning models. Chatbots, among the most widely used AI tools today, can be deliberately manipulated to corrupt their data. This tactic, known as data poisoning, involves threat actors feeding the AI misleading and malicious information, which ultimately alters its behavior. A notable example of this threat is the hacker who recently deceived a chatbot on a car dealership’s website into selling a new car for just $1.
This danger is not unprecedented. Several years ago, Google faced a similar issue when attackers compromised their Gmail spam filter. By flooding the system with millions of emails, the attackers manipulated the filter’s behavior, disrupting its ability to accurately classify spam.
Conclusion:
AI is rapidly transforming the cybersecurity landscape, providing both powerful defenses and introducing new risks. AI equips security professionals with advanced tools to detect, prevent, and respond to threats more effectively. However, it also enables cybercriminals to escalate the volume and sophistication of their attacks.
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t be. VENZA is here to help. As hospitality data protection experts, our Security Team skillfully navigates hoteliers through the complexities of managing risks associated with new technologies like AI. In partnership with us, your company can get started in as little as one month.
***
Take VENZA’s free Phishing Test to assess gaps in your human firewall today!

Training your personnel to recognize and report phishing attempts is essential to protecting your guests and their data. Get started by determining your risk and readiness level using this free tool.
***
Want to stay informed? Subscribe to the free VENZA Echo now. You’ll receive a monthly digest with the highlights of our weekly article series and important product updates and news from VENZA.
